Abstract
Purpose: This study was aimed to evaluate ocular abnormalities by using optical coherence tomography (OCT) in children with sickle cell disease (SCD) and to search the relationship between OCT and clinical findings.
Methods:The study included 108 eyes of 54 SCD patients as well as 110 eyes of 55 healthy subjects with no ocular pathology as a control group. A complete ophthalmologic examination was performed. Pupillary dilation was induced and macular sections were obtained with spectral domain OCT. Macular sections were evaluated according to the ETDRS map. Inner and outer retinal thicknesses were measured using the software in the device.
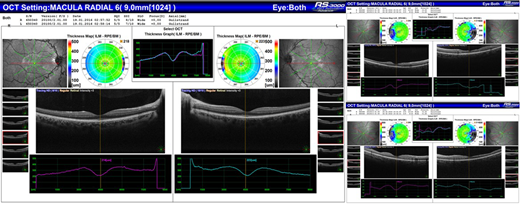
Results:Foveal splaying, temporal thinning of retinal thickness, and vascular tortuosity were found to be significantly higher in the patient group than the control group (p <0.0001 for all three parameters)(Figure-1).The foveal diameter (1592.39 ± 175.56 μ) was significantly increased in the patient group compared to the control group (1391.01 ± 175.56 μ) (p<0.0001) and the foveal depth was significantly decreased in the patient group (121.15 ± 26.83 μ) compared to the control group (146.1 ± 12.25 μ) (p<0.0001). The mean total retinal thickness was 253.53 ± 22.31 μ in the patient group and 261.03 ± 18.48 μ in the control group and the difference was statistically significant (p = 0.007). Likewise, central retinal thickness was significantly decreased in the patient group (219.35 ± 10.53 μ) compared to the control group (235.32 ± 12.51 μ) (p <0.0001).
Conclusions:Our study suggests that subclinical retinal involvement may occur in children with SCD. Foveal splaying, temporal thinning of retinal thickness, and vascular tortuosity are significant OCT findings in the children with SCD. It is seen that OCT is an important imaging method in addition to routine ophthalmologic examination to detecting ocular abnormalities in the early period and follow-up of this patient group.
Keywords:Sickle Cell Disease, Childhood, Optical Coherence Tomography
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal